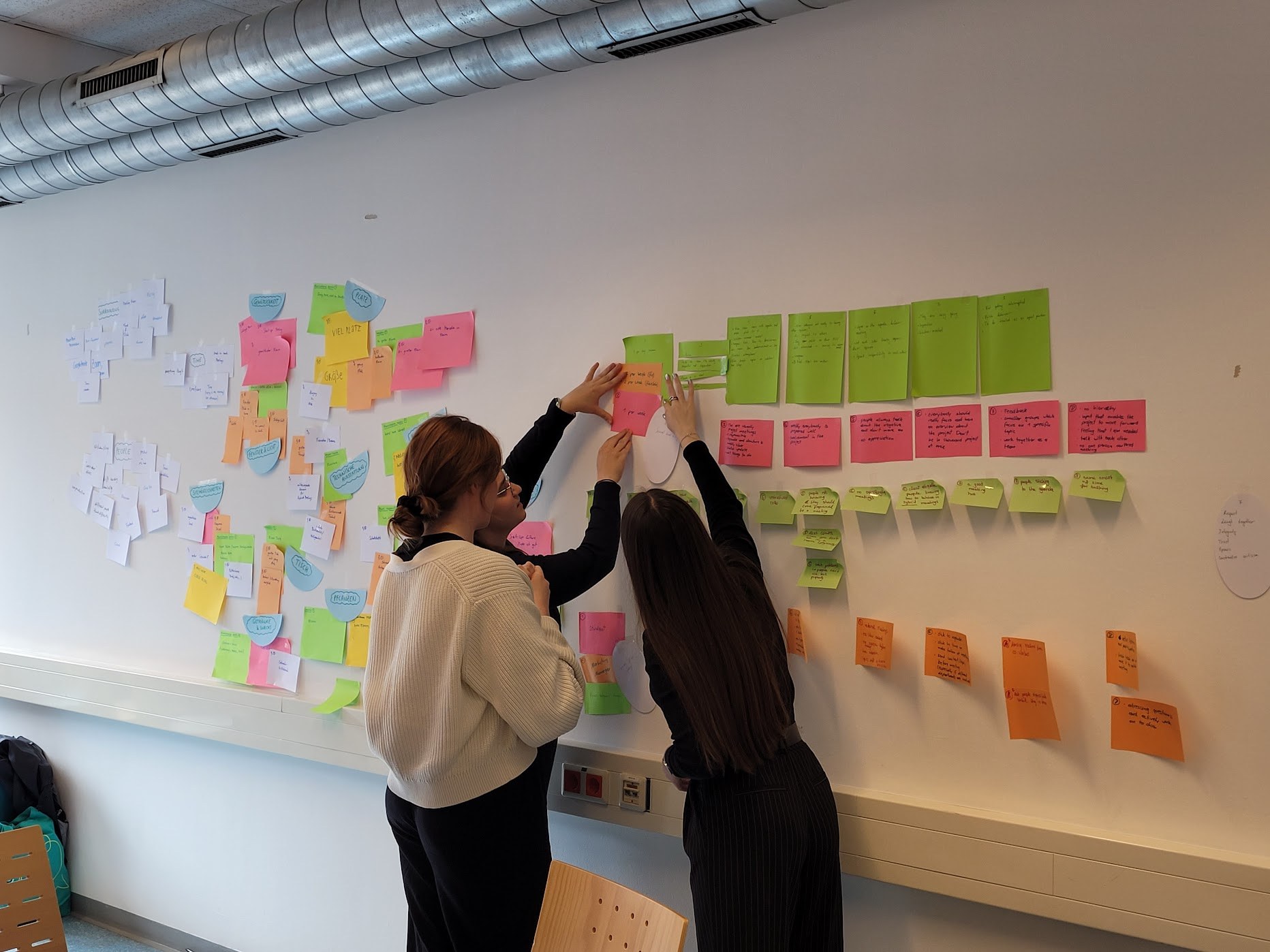
In this article, we’ll explore the design thinking process in detail and discuss its key benefits and applications.
What is Design Thinking? #
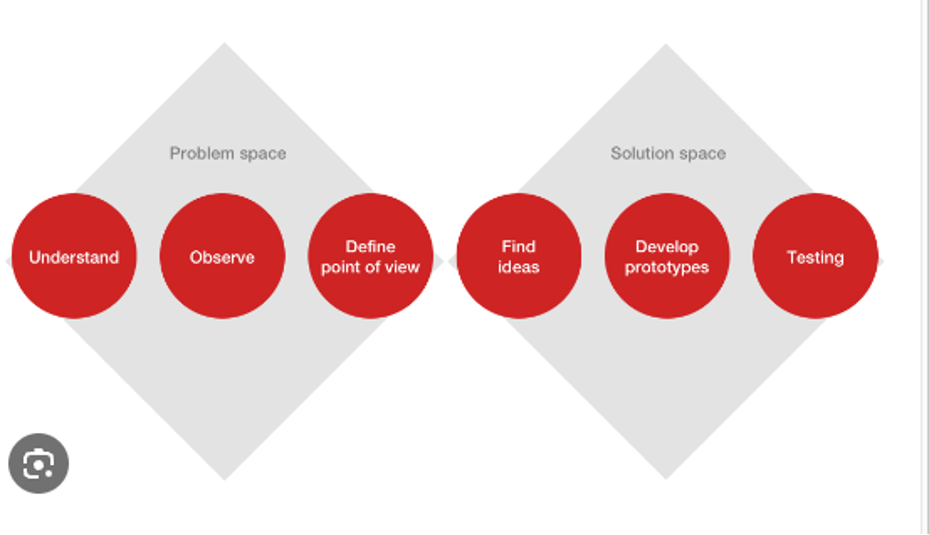
Design thinking is a solution-based approach to problem-solving that emphasizes creativity, collaboration, and user-centricity. It differs from traditional problem-solving methods by shifting the focus from the problem itself to the people affected by the solution. The design thinking process is typically divided into six key stages:
- Understand
- Observe
- Point of view
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
These stages are not always linear, and it is possible to go one or more stages back, if needed.
“Everyone designs who devises courses of action aimed at changing existing situations into preferred ones.”
Benefits of Design Thinking #
User-centricity
Design thinking places the user at the center of the solution finding process, ensuring that the final solution meets their needs and expectations.
Creativity and innovation
By encouraging divergent thinking and challenging assumptions, design thinking fosters creativity and enables teams to develop innovative solutions.
Collaboration and cross-functional teamwork
Design thinking promotes collaboration among diverse team members and different departments and encourages the exchange of ideas.
Iterative and adaptive approach
The iterative nature of design thinking allows teams to learn from failures, adapt their solutions, and continuously improve.
Competitive advantage
Companies that embrace design thinking have been shown to consistently outperform their competitors.
Applications of Design Thinking
Design thinking can be applied to a wide range of problems and industries, from product development and service design to business model innovation and social impact initiatives.
Product development
Design thinking helps teams create products that are desirable, feasible, and viable by focusing on user needs and iteratively testing ideas.
Service design
Design thinking can be used to improve existing services or create new ones by understanding the user journey and identifying pain points.
Business model innovation
Design thinking can help companies reinvent their business models by challenging assumptions and exploring new opportunities.
Social impact initiatives
Design thinking has been applied to tackle complex social problems, such as poverty, education, and healthcare by involving stakeholders and focusing on human-centered solutions.
The Ground rules of Design Thinking #
Especially when it comes to the ideation process:
- Fail fast and fail often!
- Be visual!
- Go for Quantity!
- Encourage wild Ideas!
- Stay focused on topic!
- One Conversation at a time!
- Defer judgement!
Now that we know the basic rules, we can take care of the individual steps of the process.
The Six Stages of Design Thinking #
Understand
The first step is to understand the problem, based on for example a concept Map. However, there are also other methods like Desktop research, etc. Answers about what exactly it is about, how everything is connected and what is included or not included have to be answered to create a specific focus and expansion of perception. These answers lead to a systematic organization of the topic.
This is all about “How to become an expert fast”. Through talking to experts in the field, market analyses, whitepapers or social media you can get deeper insights and become an expert quickly.
Observe
The second stage involves developing a deep understanding of the user’s needs, experiences, and pain points. This is achieved through user research, observation, interviews or focus groups and immersion in the user’s context (step in the shoes of others).
Point of View
In this stage, the team synthesizes the insights gathered during the research process to define the core problem or opportunity. A clear problem statement is formulated, which serves as a guide for the subsequent stages. Clustering the results and outputs from interviews or focus groups: target-group-orientated, activity-orientated, structured in life, available assets and risk affinity. With this knowledge, the next step is to create a Persona. This is the outcome of the observe phase.
To continue, sharpening the point of view is the next step in the Design Thinking process:
- Describe users (adjectives)
- Needs a way (verbs)
- Because (Insights)
Ideate
The Ideate stage focuses on generating a wide range of creative ideas and solutions to address the defined problem. Techniques such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and lateral thinking are employed to encourage divergent thinking and challenge assumptions.
“The aim is to generate as many ideas as possible, even ideas that you have never had before!” To generate as many ideas as possible, problem solvers need to have different perspectives during the ideate and generating idea phase: How do you personally solve the problem? How would James Bond solve your problem/question? Or Harry Potter? Or Darth Vader? … The many ideas are now being clustered into different categories, which could be market potential, most radical, best to implement, …
Prototype
The most promising ideas are selected and transformed into tangible representations, such as sketches, models, or mock-ups. Prototyping allows the team to experiment with different solutions and gather feedback from users.
Test
In the final stage, the prototypes are tested with users to gather feedback and insights. This stage helps identify areas for improvement and refine the solution. Testing may lead to further iterations of the design thinking process, as the team revisits earlier stages to refine their ideas.
Implementing Design Thinking #
Implementing design thinking effectively requires a shift in mindset and culture within an organization. Leaders must foster an environment that encourages experimentation, learning from failures, and user-centric thinking. Design thinking workshops are a popular way to apply the methodology to specific problems. These design thinking workshops bring together cross-functional teams to work through the design thinking process and develop innovative solutions.
Conclusion #
Design thinking offers a powerful approach to problem-solving that prioritizes user needs, encourages creativity, and promotes collaboration. By embracing the design thinking process, organizations can develop innovative solutions, gain a competitive advantage and make a positive impact on the world around them. As you embark on your own design thinking journey, remember to stay curious, embrace ambiguity, and continuously learn from your experiences. By following the design thinking process and adapting it to your specific context, you can unlock the power of human-centered innovation and drive meaningful change.
Where to go from here #
References #
Brannen, V. (2024, 14-15. May). Presentation slides
This article is a student-written report on a part of the course Design Thinking in the 2nd semester of the M.A. program in content strategy. It has been authorized by the instructor Vera Brannen.

